Mega Dino World Genz Map
Click Each Location On The Map For More Facts
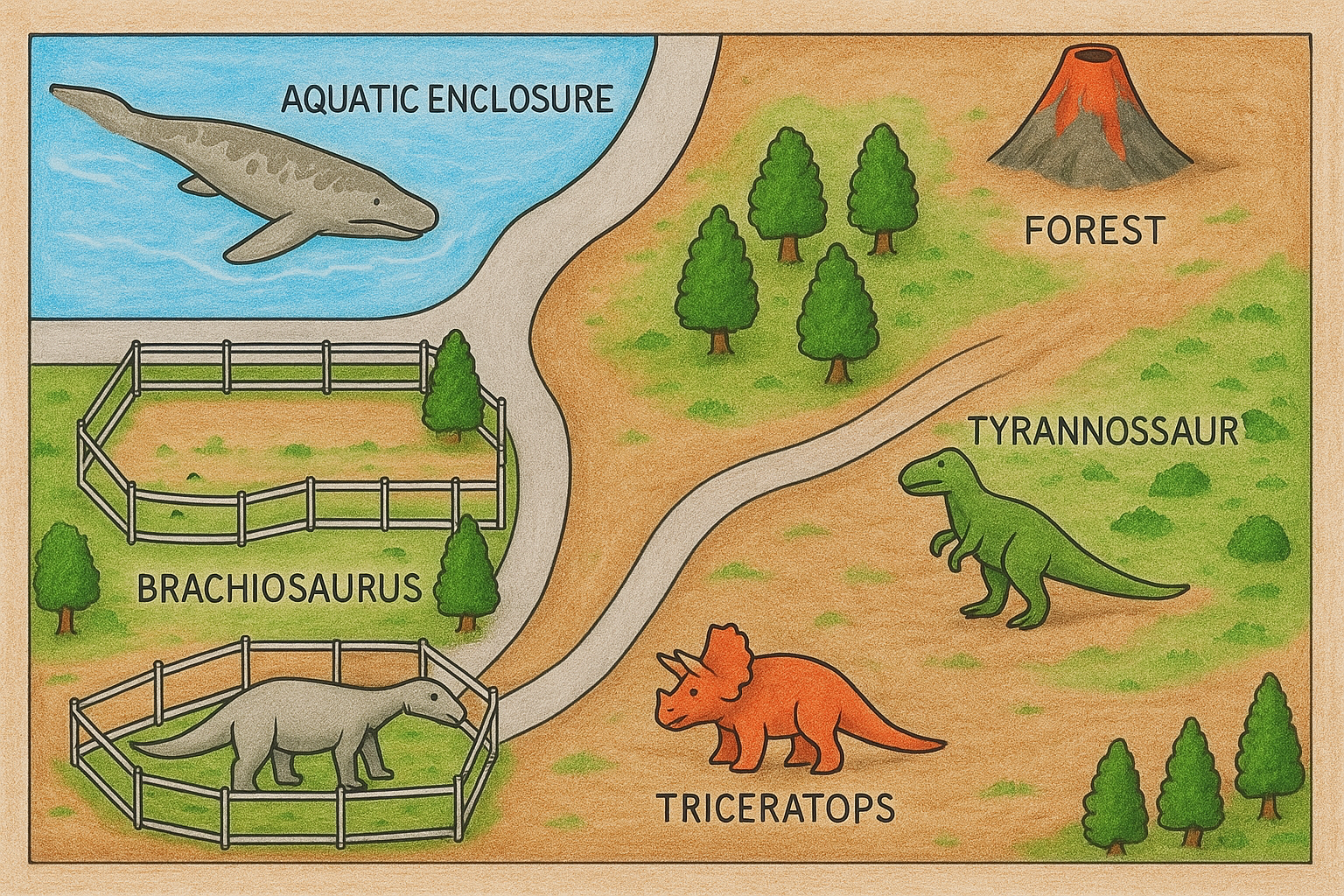
Mosasaurus
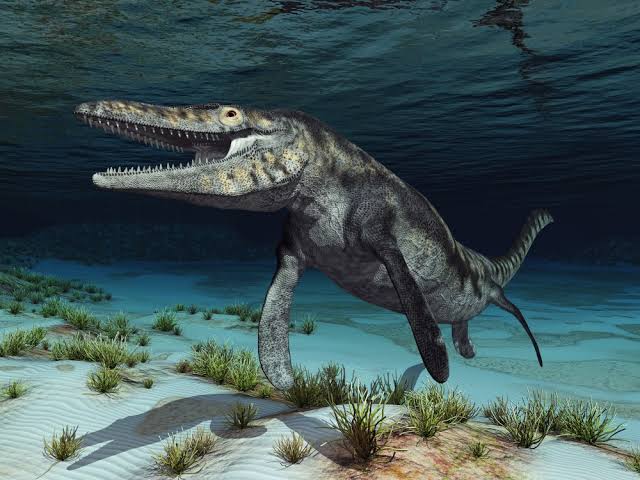

Mosasaurus was a massive, marine reptile that lived during the Late Cretaceous period, around 82 to 66 million years ago. It's one of the largest members of the mosasaur family—a group of powerful ocean-dwelling predators that dominated the seas in the age of the dinosaurs.
🦈 Basic Facts:
-
Scientific name: Mosasaurus hoffmannii (type species)
-
Length: Up to 50 feet (15 meters) long
-
Weight: Around 15,000 kg (33,000 lbs) or more
-
Habitat: Warm, shallow seas (e.g., the Western Interior Seaway in North America)
-
Diet: Carnivorous—ate fish, birds, ammonites, other marine reptiles, and possibly even smaller mosasaurs
🐊 Physical Description:
-
Body: Long and streamlined like a modern-day monitor lizard or crocodile, but fully aquatic
-
Tail: Strong, vertically flattened (like a shark's) for powerful swimming
-
Limbs: Modified into flippers; not used for walking on land
-
Jaws and teeth: Massive jaws with conical, backward-curving teeth for gripping slippery prey
-
Skull: Highly flexible, enabling it to swallow large prey whole (like a snake)
🌍 Discovery & Fossils:
-
First discovered in the Netherlands in the late 1700s (the original Mosasaurus fossil was found near the Meuse River, hence the name: "Meuse lizard")
-
Fossils have also been found in Europe, North America, South America, and Africa
🔬 Classification:
-
Kingdom: Animalia
-
Phylum: Chordata
-
Class: Reptilia
-
Order: Squamata (same as lizards and snakes)
-
Family: Mosasauridae
-
Genus: Mosasaurus
Triceratops
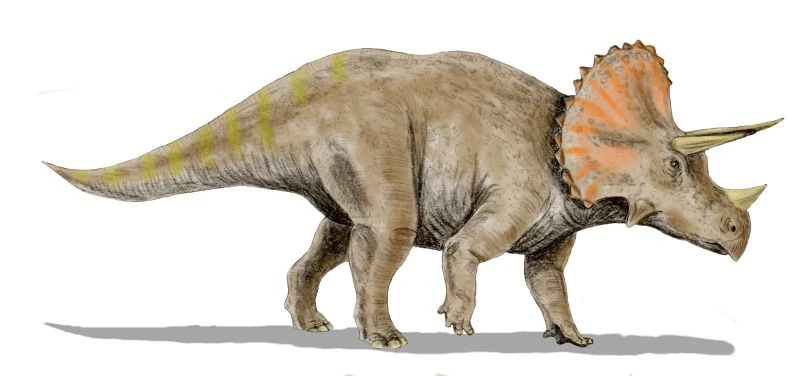
Triceratops is one of the most well-known dinosaurs, recognized for its distinctive horns and frilled skull. Here's a detailed overview:
🦖 Basic Information
-
Name: Triceratops (meaning “three-horned face”)
-
Type: Herbivorous dinosaur
-
Period: Late Cretaceous (around 68–66 million years ago)
-
Location: North America (mainly what is now western U.S. and Canada)
📏 Physical Characteristics
-
Length: Up to 30 feet (9 meters)
-
Height: About 10 feet (3 meters) at the hips
-
Weight: Estimated 6 to 12 tons
-
Skull: One of the largest of any land animal, with a frill extending over the neck
-
Horns:
-
2 long brow horns above the eyes
-
1 shorter horn on the nose
-
🌿 Diet and Behavior
-
Diet: Herbivore – fed on low-growing plants like ferns, cycads, and palms
-
Teeth: Battery of cheek teeth for grinding tough vegetation
-
Social Behavior: Unclear, but some evidence suggests they may have lived or moved in small groups
-
Defense: Used its horns and frill to defend against predators like Tyrannosaurus rex
🧠 Fun Facts
-
Triceratops vs. T. rex: Fossil evidence (bite marks on frills and horns) shows they may have fought each other
-
Frill Function: Possibly used for defense, species recognition, or attracting mates
-
Fossil Abundance: One of the most commonly found dinosaur fossils in North America
🧬 Scientific Classification
-
Kingdom: Animalia
-
Phylum: Chordata
-
Class: Reptilia
-
Order: Ornithischia
-
Family: Ceratopsidae
-
Genus: Triceratops
-
Species: Most commonly Triceratops horridus and Triceratops prorsus
Volcanoes
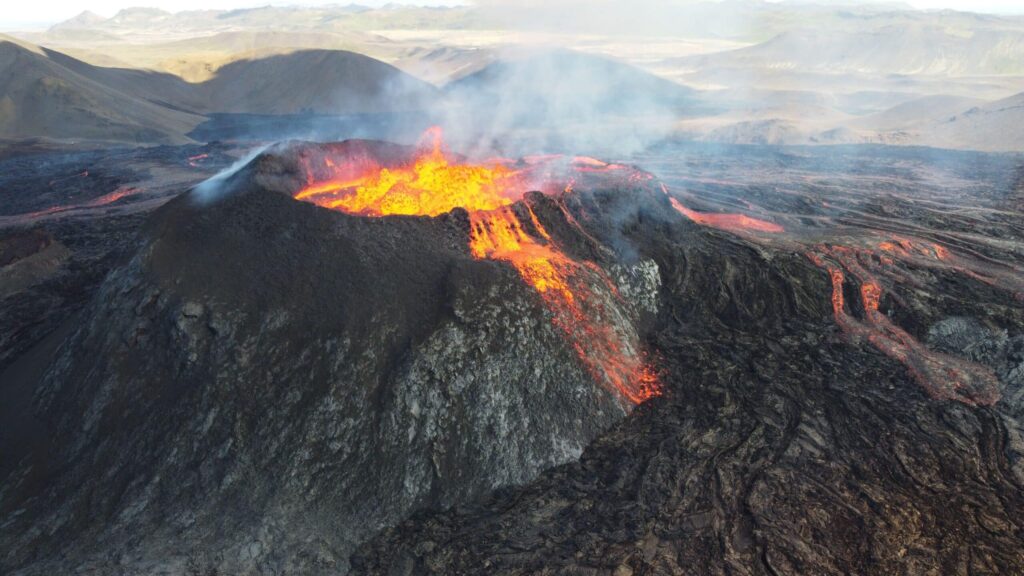

🌋 Volcanoes in the Time of Dinosaurs
🦕 When Did Dinosaurs Live?
-
Era: Mesozoic Era (about 252 to 66 million years ago)
-
Triassic Period (252–201 million years ago)
-
Jurassic Period (201–145 million years ago)
-
Cretaceous Period (145–66 million years ago)
-
Volcanoes were active during all these periods and had a major impact on the Earth and its living creatures — including dinosaurs.
🌋 What Were Volcanoes Like Back Then?
-
Types: Similar to today — shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes, and fissure eruptions
-
Locations: Found all over the world, especially near tectonic boundaries
-
Activity: Some eruptions were massive and long-lasting, covering large areas with lava and ash
🌎 Major Volcanic Events
1. Central Atlantic Magmatic Province (CAMP)
-
When: ~201 million years ago (end of the Triassic)
-
What happened: Huge volcanic eruptions lasted for thousands of years
-
Impact: Released large amounts of CO₂ and sulfur gases → caused global warming and ocean acidification
-
Result: One of Earth’s major mass extinctions, clearing the way for dinosaurs to dominate in the Jurassic
2. Deccan Traps
-
When: ~66 million years ago (end of the Cretaceous)
-
Where: Present-day India
-
What happened: Massive lava flows covered over 500,000 square km
-
Impact: May have helped wipe out the dinosaurs, along with the asteroid impact
-
Result: Contributed to the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction
🌫️ Effects of Volcanic Eruptions
-
Ash Clouds: Blocked sunlight → cooled Earth (volcanic winter)
-
Gas Emissions: CO₂ and sulfur changed climate and atmosphere
-
Lava Flows: Destroyed ecosystems and reshaped landscapes
-
Fertile Soil: After eruptions, volcanic ash created rich ground for new plant growth
🤔 Did Dinosaurs Live Near Volcanoes?
Yes — many fossils have been found in areas that were once volcanically active. Lava and ash even helped preserve dinosaur bones and footprints!
🔍 Fun Fact
Some fossilized dinosaur tracks were found in ancient volcanic ash — like dino footprints baked into ancient lava beds!
Forest

🌲 Forests in the Time of Dinosaurs
🦖 When Did Dinosaurs Live?
-
Era: Mesozoic Era (252–66 million years ago)
-
Triassic Period
-
Jurassic Period
-
Cretaceous Period
-
During these periods, Earth was covered with a wide variety of lush forests that changed over time — and they were home to many dinosaurs!
🌳 What Were Mesozoic Forests Like?
-
Warm and humid in many areas
-
No flowering plants (early on)
-
Filled with ancient trees, ferns, and conifers
-
Dinosaurs thrived in and around them
🪵 Types of Plants in Dinosaur Forests
🌴 Triassic Forests (252–201 million years ago)
-
Dominated by:
-
Cycads – palm-like plants
-
Ferns – covered the forest floor
-
Conifers – tall evergreen trees
-
Ginkgos – broad-leaf trees still around today
-
-
No flowers or grass yet!
🌲 Jurassic Forests (201–145 million years ago)
-
Lush, green, and moist
-
Huge tree ferns and tall conifer trees
-
Still no flowers, but plants began evolving
-
Ideal habitat for long-necked dinosaurs like Brachiosaurus
🌺 Cretaceous Forests (145–66 million years ago)
-
First flowering plants (angiosperms) appeared!
-
Forests became more diverse
-
Magnolias, figs, and early hardwood trees
-
Attracting new plant-eating dinosaurs and insects
🦕 Dinosaurs That Lived in Forests
-
Stegosaurus – grazed on low plants and ferns
-
Triceratops – lived near woodland edges, fed on shrubs
-
Velociraptor – hunted in dry, forested areas
-
Sauropods – ate leaves from tall conifers
-
Ankylosaurs – loved forest undergrowth
🌿 Why Forests Were Important
-
🌡️ Helped control Earth’s climate (just like today)
-
🦎 Provided food and shelter for dinosaurs
-
🐞 Home to ancient insects, mammals, and birds
-
🪦 Fossilized forests help scientists learn about ancient ecosystems
🌍 Where Were These Forests?
-
All over the world!
Continental drift and a warmer global climate meant even polar regions had forests — with no ice caps!
🔍 Fun Fact
Some fossil forests have been found still standing upright — trees turned to stone after volcanic ash buried them!
Forest

🌲 Forests in the Time of Dinosaurs
🦖 When Did Dinosaurs Live?
-
Era: Mesozoic Era (252–66 million years ago)
-
Triassic Period
-
Jurassic Period
-
Cretaceous Period
-
During these periods, Earth was covered with a wide variety of lush forests that changed over time — and they were home to many dinosaurs!
🌳 What Were Mesozoic Forests Like?
-
Warm and humid in many areas
-
No flowering plants (early on)
-
Filled with ancient trees, ferns, and conifers
-
Dinosaurs thrived in and around them
🪵 Types of Plants in Dinosaur Forests
🌴 Triassic Forests (252–201 million years ago)
-
Dominated by:
-
Cycads – palm-like plants
-
Ferns – covered the forest floor
-
Conifers – tall evergreen trees
-
Ginkgos – broad-leaf trees still around today
-
-
No flowers or grass yet!
🌲 Jurassic Forests (201–145 million years ago)
-
Lush, green, and moist
-
Huge tree ferns and tall conifer trees
-
Still no flowers, but plants began evolving
-
Ideal habitat for long-necked dinosaurs like Brachiosaurus
🌺 Cretaceous Forests (145–66 million years ago)
-
First flowering plants (angiosperms) appeared!
-
Forests became more diverse
-
Magnolias, figs, and early hardwood trees
-
Attracting new plant-eating dinosaurs and insects
🦕 Dinosaurs That Lived in Forests
-
Stegosaurus – grazed on low plants and ferns
-
Triceratops – lived near woodland edges, fed on shrubs
-
Velociraptor – hunted in dry, forested areas
-
Sauropods – ate leaves from tall conifers
-
Ankylosaurs – loved forest undergrowth
🌿 Why Forests Were Important
-
🌡️ Helped control Earth’s climate (just like today)
-
🦎 Provided food and shelter for dinosaurs
-
🐞 Home to ancient insects, mammals, and birds
-
🪦 Fossilized forests help scientists learn about ancient ecosystems
🌍 Where Were These Forests?
-
All over the world!
Continental drift and a warmer global climate meant even polar regions had forests — with no ice caps!
🔍 Fun Fact
Some fossil forests have been found still standing upright — trees turned to stone after volcanic ash buried them!
