FUN INTERACTIVE DINO WORLD
Explore the world of dinosaurs with interactive maps and fascinating facts about these prehistoric creatures.
Days
Hours
Minutes
Seconds
Mega Dino World Genz Map
Click Each Location On The Map For More Facts
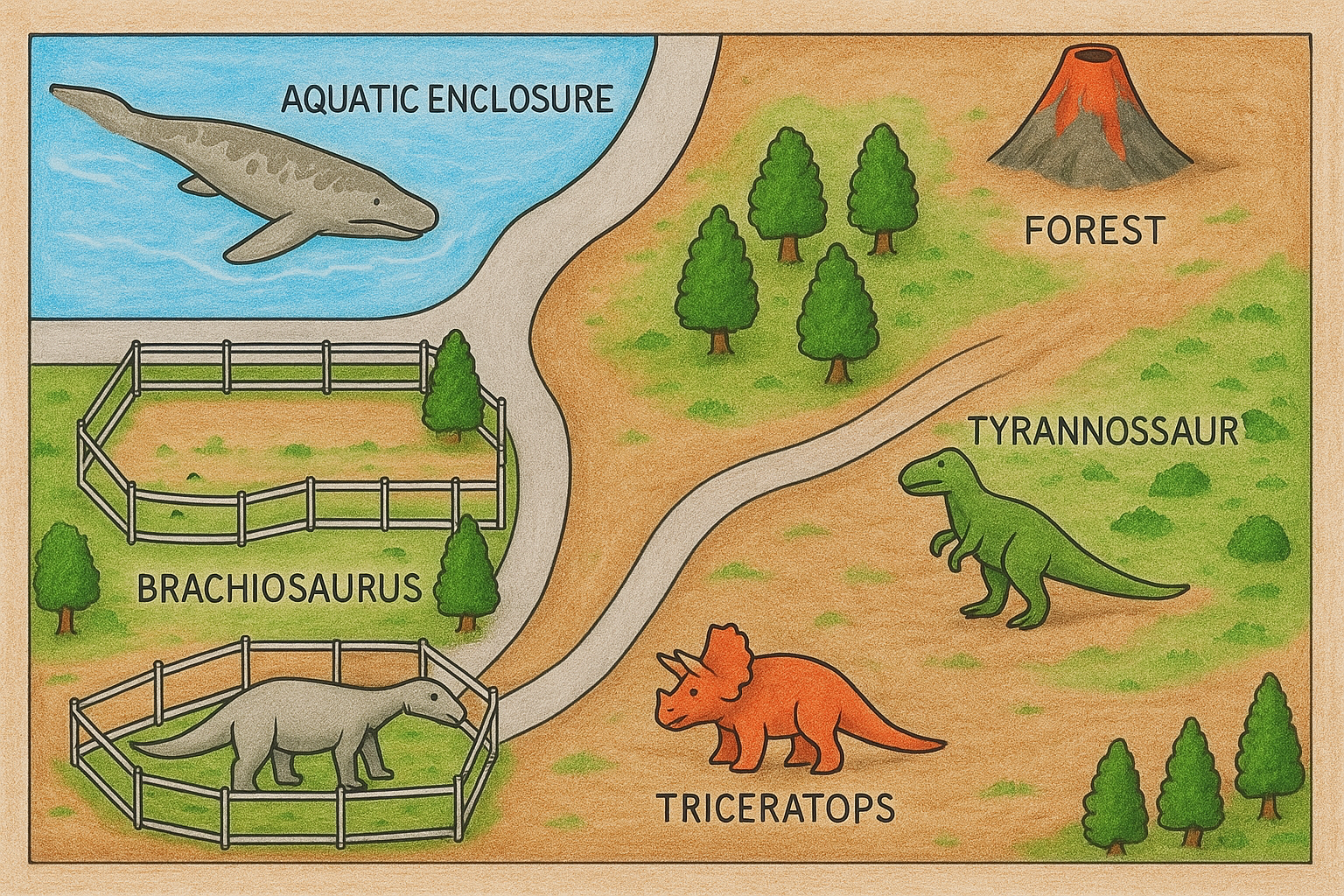
Mosasaurus
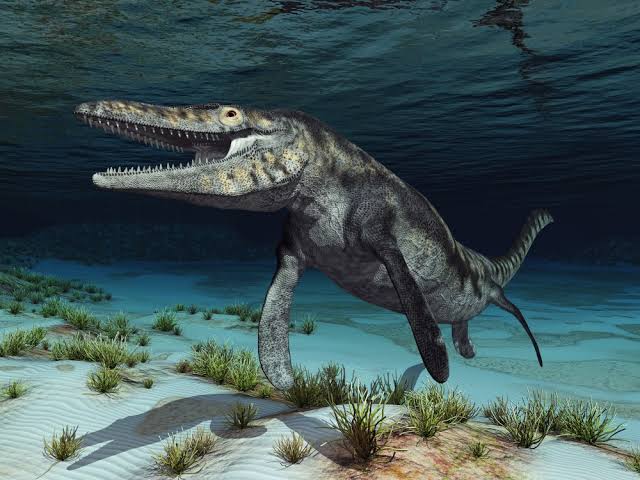

Mosasaurus was a massive, marine reptile that lived during the Late Cretaceous period, around 82 to 66 million years ago. It's one of the largest members of the mosasaur family—a group of powerful ocean-dwelling predators that dominated the seas in the age of the dinosaurs.
🦈 Basic Facts:
-
Scientific name: Mosasaurus hoffmannii (type species)
-
Length: Up to 50 feet (15 meters) long
-
Weight: Around 15,000 kg (33,000 lbs) or more
-
Habitat: Warm, shallow seas (e.g., the Western Interior Seaway in North America)
-
Diet: Carnivorous—ate fish, birds, ammonites, other marine reptiles, and possibly even smaller mosasaurs
🐊 Physical Description:
-
Body: Long and streamlined like a modern-day monitor lizard or crocodile, but fully aquatic
-
Tail: Strong, vertically flattened (like a shark's) for powerful swimming
-
Limbs: Modified into flippers; not used for walking on land
-
Jaws and teeth: Massive jaws with conical, backward-curving teeth for gripping slippery prey
-
Skull: Highly flexible, enabling it to swallow large prey whole (like a snake)
🌍 Discovery & Fossils:
-
First discovered in the Netherlands in the late 1700s (the original Mosasaurus fossil was found near the Meuse River, hence the name: "Meuse lizard")
-
Fossils have also been found in Europe, North America, South America, and Africa
🔬 Classification:
-
Kingdom: Animalia
-
Phylum: Chordata
-
Class: Reptilia
-
Order: Squamata (same as lizards and snakes)
-
Family: Mosasauridae
-
Genus: Mosasaurus
Triceratops
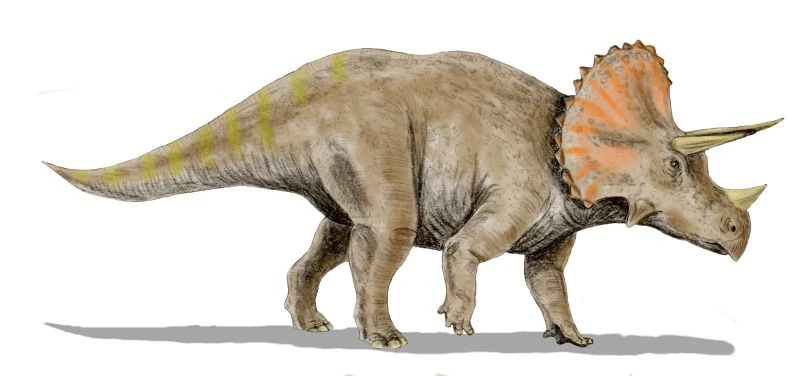
Triceratops is one of the most well-known dinosaurs, recognized for its distinctive horns and frilled skull. Here's a detailed overview:
🦖 Basic Information
-
Name: Triceratops (meaning “three-horned face”)
-
Type: Herbivorous dinosaur
-
Period: Late Cretaceous (around 68–66 million years ago)
-
Location: North America (mainly what is now western U.S. and Canada)
📏 Physical Characteristics
-
Length: Up to 30 feet (9 meters)
-
Height: About 10 feet (3 meters) at the hips
-
Weight: Estimated 6 to 12 tons
-
Skull: One of the largest of any land animal, with a frill extending over the neck
-
Horns:
-
2 long brow horns above the eyes
-
1 shorter horn on the nose
-
🌿 Diet and Behavior
-
Diet: Herbivore – fed on low-growing plants like ferns, cycads, and palms
-
Teeth: Battery of cheek teeth for grinding tough vegetation
-
Social Behavior: Unclear, but some evidence suggests they may have lived or moved in small groups
-
Defense: Used its horns and frill to defend against predators like Tyrannosaurus rex
🧠 Fun Facts
-
Triceratops vs. T. rex: Fossil evidence (bite marks on frills and horns) shows they may have fought each other
-
Frill Function: Possibly used for defense, species recognition, or attracting mates
-
Fossil Abundance: One of the most commonly found dinosaur fossils in North America
🧬 Scientific Classification
-
Kingdom: Animalia
-
Phylum: Chordata
-
Class: Reptilia
-
Order: Ornithischia
-
Family: Ceratopsidae
-
Genus: Triceratops
-
Species: Most commonly Triceratops horridus and Triceratops prorsus
Volcanoes
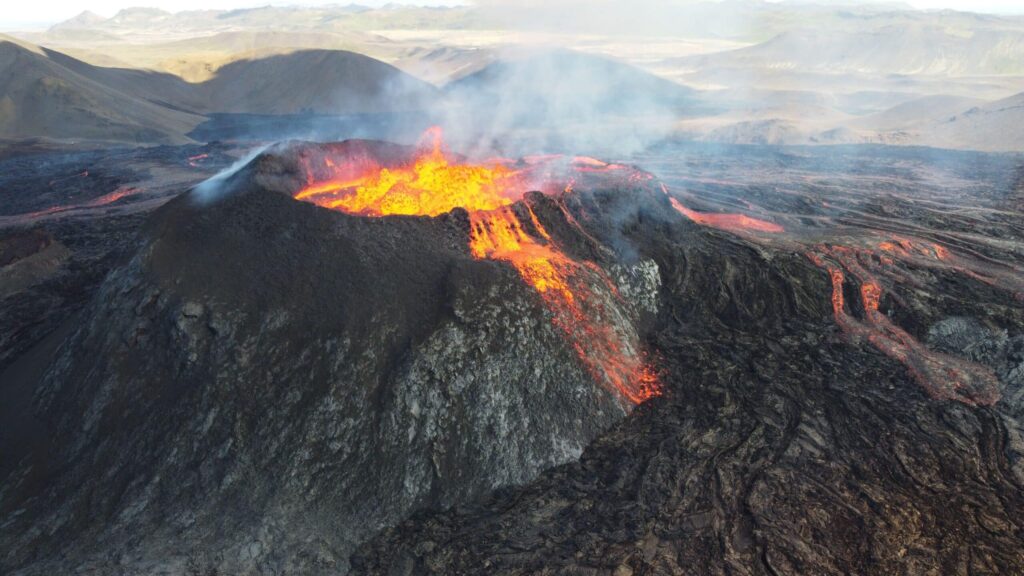

🌋 Volcanoes in the Time of Dinosaurs
🦕 When Did Dinosaurs Live?
-
Era: Mesozoic Era (about 252 to 66 million years ago)
-
Triassic Period (252–201 million years ago)
-
Jurassic Period (201–145 million years ago)
-
Cretaceous Period (145–66 million years ago)
-
Volcanoes were active during all these periods and had a major impact on the Earth and its living creatures — including dinosaurs.
🌋 What Were Volcanoes Like Back Then?
-
Types: Similar to today — shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes, and fissure eruptions
-
Locations: Found all over the world, especially near tectonic boundaries
-
Activity: Some eruptions were massive and long-lasting, covering large areas with lava and ash
🌎 Major Volcanic Events
1. Central Atlantic Magmatic Province (CAMP)
-
When: ~201 million years ago (end of the Triassic)
-
What happened: Huge volcanic eruptions lasted for thousands of years
-
Impact: Released large amounts of CO₂ and sulfur gases → caused global warming and ocean acidification
-
Result: One of Earth’s major mass extinctions, clearing the way for dinosaurs to dominate in the Jurassic
2. Deccan Traps
-
When: ~66 million years ago (end of the Cretaceous)
-
Where: Present-day India
-
What happened: Massive lava flows covered over 500,000 square km
-
Impact: May have helped wipe out the dinosaurs, along with the asteroid impact
-
Result: Contributed to the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction
🌫️ Effects of Volcanic Eruptions
-
Ash Clouds: Blocked sunlight → cooled Earth (volcanic winter)
-
Gas Emissions: CO₂ and sulfur changed climate and atmosphere
-
Lava Flows: Destroyed ecosystems and reshaped landscapes
-
Fertile Soil: After eruptions, volcanic ash created rich ground for new plant growth
🤔 Did Dinosaurs Live Near Volcanoes?
Yes — many fossils have been found in areas that were once volcanically active. Lava and ash even helped preserve dinosaur bones and footprints!
🔍 Fun Fact
Some fossilized dinosaur tracks were found in ancient volcanic ash — like dino footprints baked into ancient lava beds!
Forest

🌲 Forests in the Time of Dinosaurs
🦖 When Did Dinosaurs Live?
-
Era: Mesozoic Era (252–66 million years ago)
-
Triassic Period
-
Jurassic Period
-
Cretaceous Period
-
During these periods, Earth was covered with a wide variety of lush forests that changed over time — and they were home to many dinosaurs!
🌳 What Were Mesozoic Forests Like?
-
Warm and humid in many areas
-
No flowering plants (early on)
-
Filled with ancient trees, ferns, and conifers
-
Dinosaurs thrived in and around them
🪵 Types of Plants in Dinosaur Forests
🌴 Triassic Forests (252–201 million years ago)
-
Dominated by:
-
Cycads – palm-like plants
-
Ferns – covered the forest floor
-
Conifers – tall evergreen trees
-
Ginkgos – broad-leaf trees still around today
-
-
No flowers or grass yet!
🌲 Jurassic Forests (201–145 million years ago)
-
Lush, green, and moist
-
Huge tree ferns and tall conifer trees
-
Still no flowers, but plants began evolving
-
Ideal habitat for long-necked dinosaurs like Brachiosaurus
🌺 Cretaceous Forests (145–66 million years ago)
-
First flowering plants (angiosperms) appeared!
-
Forests became more diverse
-
Magnolias, figs, and early hardwood trees
-
Attracting new plant-eating dinosaurs and insects
🦕 Dinosaurs That Lived in Forests
-
Stegosaurus – grazed on low plants and ferns
-
Triceratops – lived near woodland edges, fed on shrubs
-
Velociraptor – hunted in dry, forested areas
-
Sauropods – ate leaves from tall conifers
-
Ankylosaurs – loved forest undergrowth
🌿 Why Forests Were Important
-
🌡️ Helped control Earth’s climate (just like today)
-
🦎 Provided food and shelter for dinosaurs
-
🐞 Home to ancient insects, mammals, and birds
-
🪦 Fossilized forests help scientists learn about ancient ecosystems
🌍 Where Were These Forests?
-
All over the world!
Continental drift and a warmer global climate meant even polar regions had forests — with no ice caps!
🔍 Fun Fact
Some fossil forests have been found still standing upright — trees turned to stone after volcanic ash buried them!
Forest

🌲 Forests in the Time of Dinosaurs
🦖 When Did Dinosaurs Live?
-
Era: Mesozoic Era (252–66 million years ago)
-
Triassic Period
-
Jurassic Period
-
Cretaceous Period
-
During these periods, Earth was covered with a wide variety of lush forests that changed over time — and they were home to many dinosaurs!
🌳 What Were Mesozoic Forests Like?
-
Warm and humid in many areas
-
No flowering plants (early on)
-
Filled with ancient trees, ferns, and conifers
-
Dinosaurs thrived in and around them
🪵 Types of Plants in Dinosaur Forests
🌴 Triassic Forests (252–201 million years ago)
-
Dominated by:
-
Cycads – palm-like plants
-
Ferns – covered the forest floor
-
Conifers – tall evergreen trees
-
Ginkgos – broad-leaf trees still around today
-
-
No flowers or grass yet!
🌲 Jurassic Forests (201–145 million years ago)
-
Lush, green, and moist
-
Huge tree ferns and tall conifer trees
-
Still no flowers, but plants began evolving
-
Ideal habitat for long-necked dinosaurs like Brachiosaurus
🌺 Cretaceous Forests (145–66 million years ago)
-
First flowering plants (angiosperms) appeared!
-
Forests became more diverse
-
Magnolias, figs, and early hardwood trees
-
Attracting new plant-eating dinosaurs and insects
🦕 Dinosaurs That Lived in Forests
-
Stegosaurus – grazed on low plants and ferns
-
Triceratops – lived near woodland edges, fed on shrubs
-
Velociraptor – hunted in dry, forested areas
-
Sauropods – ate leaves from tall conifers
-
Ankylosaurs – loved forest undergrowth
🌿 Why Forests Were Important
-
🌡️ Helped control Earth’s climate (just like today)
-
🦎 Provided food and shelter for dinosaurs
-
🐞 Home to ancient insects, mammals, and birds
-
🪦 Fossilized forests help scientists learn about ancient ecosystems
🌍 Where Were These Forests?
-
All over the world!
Continental drift and a warmer global climate meant even polar regions had forests — with no ice caps!
🔍 Fun Fact
Some fossil forests have been found still standing upright — trees turned to stone after volcanic ash buried them!
